

Ossiculoplasty is typically performed to treat issues such as damage or erosion of the ossicles due to chronic ear infections, trauma, congenital malformations, or other middle ear diseases. The goal of the procedure is to improve hearing by restoring the normal function of the ossicular chain.
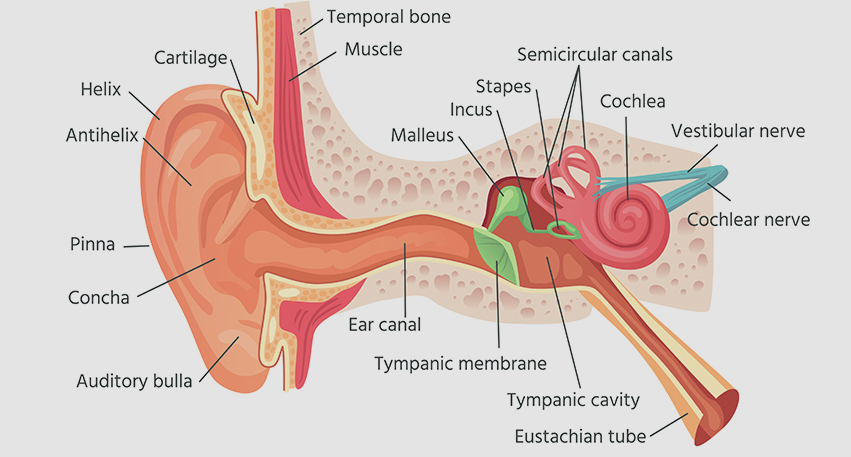
The procedure involves accessing the middle ear, often directly through the ear canal or by making a small incision behind the ear. The surgeon may use various techniques, including the placement of prosthetic devices or grafts, to repair or replace damaged ossicles.
The primary benefit of Ossiculoplasty is the potential improvement in hearing. By reconstructing the ossicular chain, sound transmission can be restored, leading to enhanced auditory function.
As with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks involved, such as infection, changes in taste, or failure of the graft or prosthesis.
Recovery after ossiculoplasty varies, but most individuals can expect some improvement in hearing over time. Patients will need to follow postoperative care instructions, which may include restrictions on certain activities and medications to prevent infection.
Patients should contact their doctor if they experience persistent pain, signs of infection, or any worsening of hearing after ossiculoplasty. Regular follow-up appointments will allow the doctor to address any concerns and track the long-term outcomes of the procedure.

